Cancer is a leading cause of death worldwide, but advancements in treatment are offering new hope. Early detection and proper treatment can significantly improve survival rates.
1. What is Cancer?
Cancer is the uncontrolled growth of abnormal cells in the body. Usually, cells grow, divide, and die in a controlled manner. However, when this process goes wrong, cells grow uncontrollably, forming tumors or spreading through the bloodstream to other body parts (metastasis). Cancer can develop almost anywhere, affecting different organs and tissues.

Key Points:
Tumors can be benign (non-cancerous) or malignant (cancerous).
Metastasis refers to cancer spreading to distant parts of the body.
2. Common Symptoms of Cancer
Symptoms of cancer vary depending on the type and location of the cancer. However, there are general signs that may indicate the presence of cancer. Recognizing these symptoms early can lead to timely medical attention and potentially life-saving interventions.

General Symptoms of Cancer:
Unexplained weight loss: A sudden drop in weight without changes in diet or exercise.
Fatigue: Persistent tiredness that doesn’t improve with rest.
Fever: Prolonged fever without an apparent cause.
Pain: Can occur in various body parts, especially in advanced stages.
Skin changes: Yellowing, darkening, or redness, as well as sores that don’t heal.
Lumps or swelling: Unexplained lumps or thickening, especially in the breast, testicles, or lymph nodes.
Persistent cough or hoarseness can be an early sign of lung or throat cancer.
Changes in bowel or bladder habits: Diarrhea, constipation, blood in stool, or difficulty urinating.
Unusual bleeding or discharge: Blood in urine, stool, or abnormal vaginal bleeding.
It’s important to note that other conditions can also cause these symptoms. A healthcare professional should evaluate persistent or unexplained symptoms.
Read more: The Center for Hematology: Advancing Blood Disorder Treatments with Precision
3. Causes and Risk Factors of Cancer
The exact cause of cancer is not always clear, but a combination of genetic, lifestyle, and environmental factors often contributes to its development. Understanding these causes helps individuals take preventive measures and manage risk.
Genetic Factors:
Some people are born with genetic mutations that increase their likelihood of developing cancer. For example, mutations in the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes significantly raise the risk of breast and ovarian cancers.
Lifestyle Factors:
Smoking: A significant risk factor for lung, mouth, throat, and several other cancers.
Diet: Poor diet, high in processed foods and low in fruits and vegetables, may increase the risk.
Alcohol consumption: Heavy drinking has been linked to cancers of the liver, breast, and esophagus.
Physical inactivity and obesity: Being overweight or inactive raises the risk of many cancers, including colon, breast, and endometrial cancer.
Environmental Factors:
Exposure to carcinogens: Long-term exposure to substances like asbestos, radiation, and certain chemicals can trigger cancer development.
Infections: Certain viruses, such as Human Papillomavirus (HPV), Hepatitis B, and Epstein-Barr, can lead to cancer.
UV radiation: Prolonged exposure to the sun or tanning beds increases the risk of skin cancer.
Your strength isn’t measured by the size of the battle but by the courage you show every single day.
4. Types of Cancer
There are more than 100 types of cancer, but they are generally grouped into five main categories:
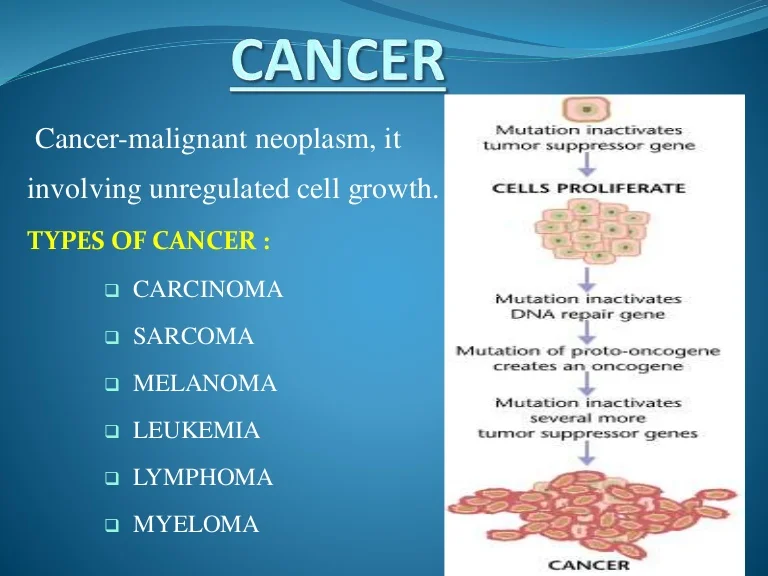
1. Carcinomas
The most common type affects the skin, lungs, breasts, pancreas, and other organs. It begins in the epithelial cells that line the body’s surfaces.
2. Sarcomas
These cancers develop in the connective tissues, such as bones, muscles, fat, and blood vessels.
3. Leukemias
A type of cancer that affects the blood and bone marrow, causing the overproduction of abnormal white blood cells.
4. Lymphomas
Cancer of the lymphatic system includes lymph nodes and immune cells.
5. Melanomas
A severe form of skin cancer that originates in pigment-producing melanocytes.
Each type of cancer progresses differently and responds uniquely to treatment, making an accurate diagnosis crucial for adequate care.
5. Diagnosis of Cancer
Accurate and early diagnosis is critical to improving outcomes. The diagnostic process typically includes:
Physical exams: Doctors look for lumps or other abnormalities.
Imaging tests: CT scans, MRIs, PET scans, X-rays, and ultrasounds help visualize tumors.
Biopsy: A tissue sample is removed for microscopic analysis to confirm if it’s cancerous.
Laboratory tests: Blood tests like the Complete Blood Count (CBC) can identify abnormalities related to cancers, such as leukemia.
Genetic testing: Helps identify hereditary cancer syndromes and guides personalized treatment plans.
Read more: Does Seeing a Hematologist Mean I Have Cancer?
6. Cancer Treatment Options
Cancer treatment has made significant strides over the past decade. While surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation remain standard options, newer therapies are changing the landscape of cancer care.
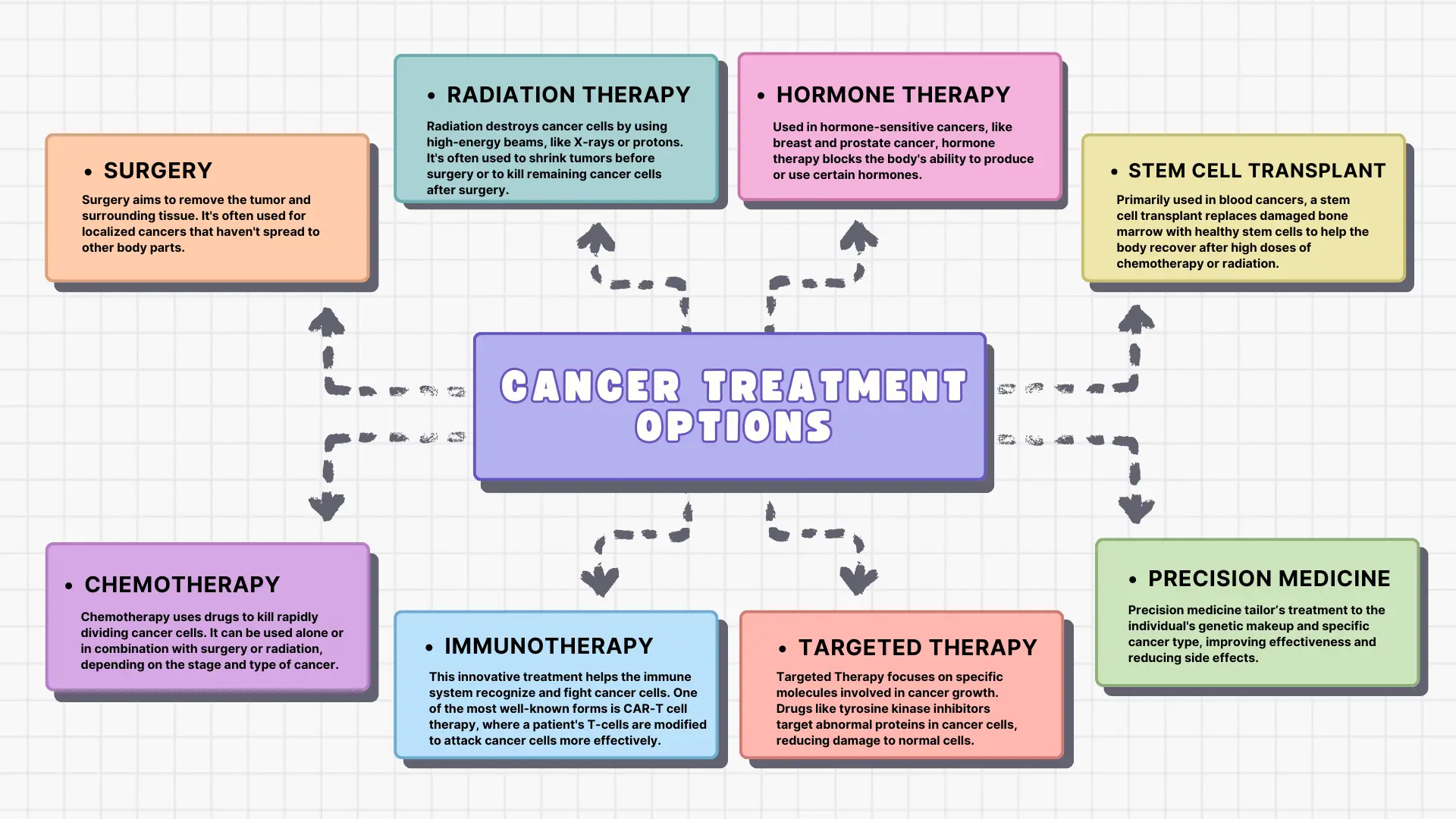
1. Surgery
Surgery aims to remove the tumor and surrounding tissue. It’s often used for localized cancers that haven’t spread to other body parts.
2. Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy uses drugs to kill rapidly dividing cancer cells. It can be used alone or in combination with surgery or radiation, depending on the stage and type of cancer.
3. Radiation Therapy
Radiation destroys cancer cells by using high-energy beams, like X-rays or protons. It’s often used to shrink tumors before surgery or to kill remaining cancer cells after surgery.
4. Immunotherapy
This innovative treatment helps the immune system recognize and fight cancer cells. One of the most well-known forms is CAR-T cell therapy, where a patient’s T-cells are modified to attack cancer cells more effectively.
5. Targeted Therapy
Targeted Therapy focuses on specific molecules involved in cancer growth. Drugs like tyrosine kinase inhibitors target abnormal proteins in cancer cells, reducing damage to normal cells.
6. Hormone Therapy
Used in hormone-sensitive cancers, like breast and prostate cancer, hormone therapy blocks the body’s ability to produce or use certain hormones.
7. Stem Cell Transplant
Primarily used in blood cancers, a stem cell transplant replaces damaged bone marrow with healthy stem cells to help the body recover after high doses of chemotherapy or radiation.
8. Precision Medicine
Precision medicine tailor’s treatment to the individual’s genetic makeup and specific cancer type, improving effectiveness and reducing side effects.
9. Clinical Trials
For some patients, participating in clinical trials offers access to cutting-edge treatments that are yet to be widely available.
Read more: AACR/ASCO Methods in Clinical Cancer Research Workshop: A Path to Innovative Clinical Trial Design
7. Prevention and Early Detection
While not all cancers can be prevented, many can be avoided by reducing risk factors:

Quit smoking to lower your risk of lung and several other cancers drastically.
Adopt a healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
Exercise regularly and maintain a healthy weight.
Limit alcohol consumption and avoid excessive sun exposure.
Get vaccinated against cancer-causing infections like HPV and hepatitis.
Regular screenings like mammograms, colonoscopies, and skin checks can catch cancer early when it’s most treatable.
8. Future of Cancer Treatment
The future of cancer treatment is promising, with ongoing research in several groundbreaking areas:
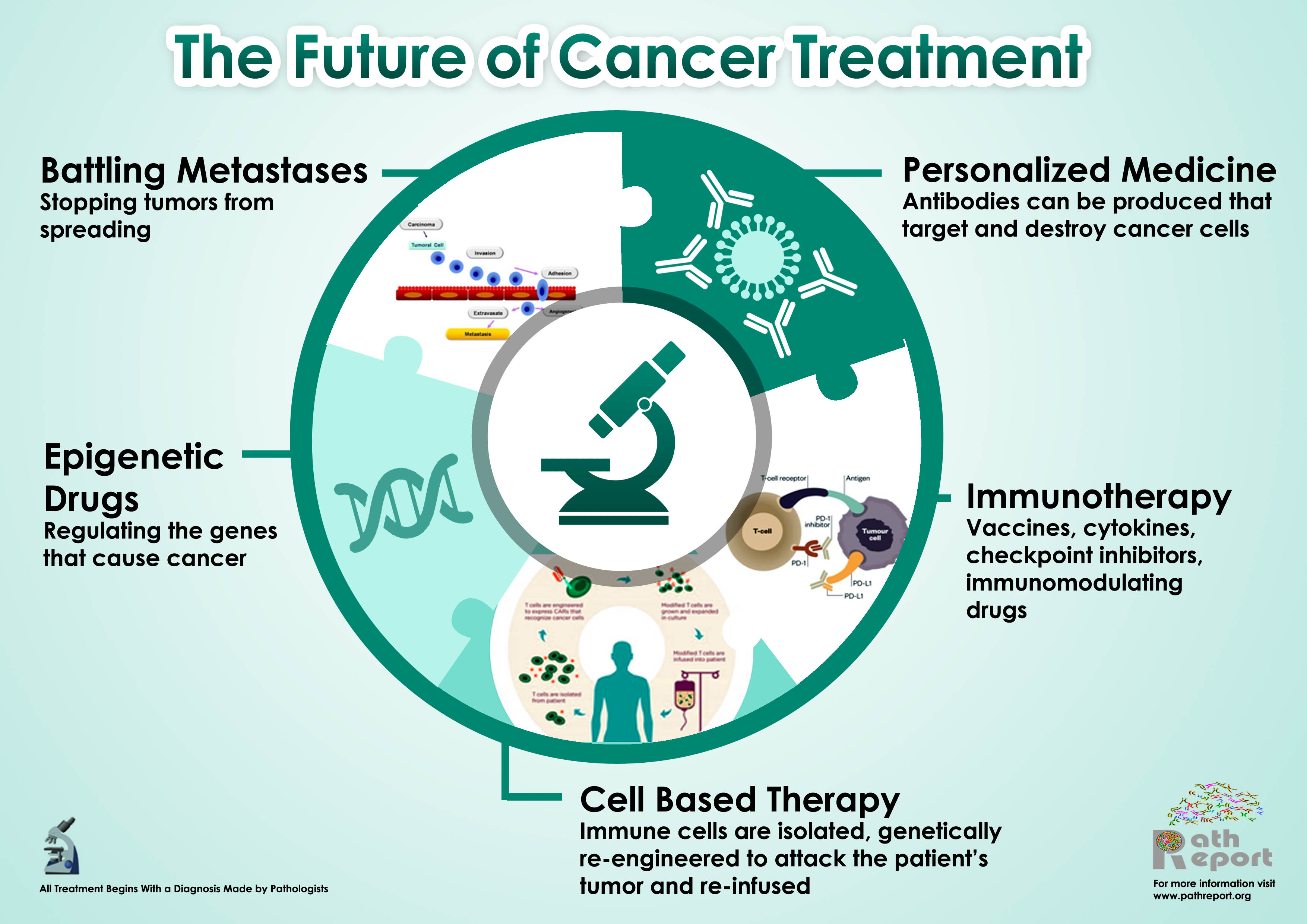
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
AI analyzes complex medical data, leading to faster diagnoses and more personalized treatment plans.
Liquid Biopsy
This noninvasive test detects cancer markers in blood samples, offering a way to monitor cancer progression and response to treatment in real-time.
Gene Therapy
Gene therapy aims to correct or replace faulty genes responsible for cancer, offering the potential for cures in certain genetic cancers.
Vaccines
Cancer vaccines, like the HPV vaccine, are preventing certain types of cancer before they develop. Research into therapeutic cancer vaccines is also underway.
Hope is the most powerful weapon in the fight against cancer. Every step forward is a victory, no matter how small.
Read more: What is Blood Disorders? Types, Syptoms and Treatment
9. Conclusion
Understanding the symptoms, causes, and types of cancer is vital for early detection and effective treatment. Cancer care is becoming more personalized and effective with modern advancements like immunotherapy, targeted therapies, and precision medicine. By staying informed and taking preventive measures, individuals can reduce risk and improve their chances of successful treatment.
Suppose you or a loved one has been diagnosed with cancer. In that case, it’s essential to seek guidance from specialists and consider all available treatment options, including the possibility of participating in clinical trials.